rfid chips in skin Mr Paumen has a chip under the skin of his left hand, and it lights up when it comes into close contact with a payment machine. A microchip was . NFC cards are designed to be read by NFC-enabled devices, such as smartphones, and the information stored on the card is encoded in a way that these devices can only understand. If .
0 · Thousands Of Swedes Are Inserting Microchips Under Their Skin
1 · The microchip implants that let you pay with your
2 · Human Microchipping: An Unbiased Look at the Pros and Cons
5. Minnesota Vikings (7-2) Minnesota is the No. 5 seed in the NFC, trailing Detroit by a game for the division lead. The Vikings are the top wild-card team in the conference.
Thousands Of Swedes Are Inserting Microchips Under Their Skin
sensors used in smart card
The microchip implants that let you pay with your
Mr Paumen has a chip under the skin of his left hand, and it lights up when it comes into close contact with a payment machine. A microchip was . Around the size of a grain of rice, the chips typically are inserted into the skin . RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already .
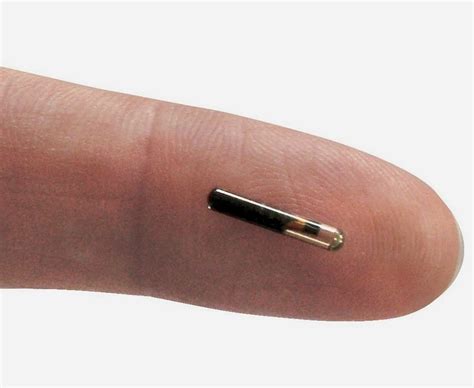
Mr Paumen has a chip under the skin of his left hand, and it lights up when it comes into close contact with a payment machine. A microchip was first implanted into a human back in 1998, but it. Around the size of a grain of rice, the chips typically are inserted into the skin just above each user's thumb, using a syringe similar to that used for giving vaccinations. RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already cheap and available, provide a digital interface to the real world centered about the holder’s identity: your ID, credit card information, bus pass, library card, and many other sources of information you currently carry in your purse/wallet can instead be stored on an .

Self-described “bio-hackers” are voluntarily injecting radio frequency identification chips under their skin, which allows them to pay for purchases by just hovering their bare hand over a scanner at a checkout counter. A chip is implanted underneath the skin between the thumb and forefinger within seconds. 32M claims it is the first company in the US to have offer implanted chip technology to employees. Microchip in Humans - Passport for everything.
shawn coffey smart card commercial
Mr Paumen has a chip under the skin of his left hand, and it lights up when it comes into close contact with a payment machine. A microchip was first implanted into a human back in 1998, but it.A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical terms, a. First, the RFID chips are passive – they can’t be tracked since they don’t emit signals. Second, in order to activate the chip implant you have to touch it to a reader; and while someone can scan it without your consent, they would have to get up close since the chips can’t be read at a distance.

Embedded under Williams’ skin is a microchip implant — an electronic circuit inside a pill-shaped glass capsule — that can be used much like a contactless credit card. Mr Paumen has a chip under the skin of his left hand, and it lights up when it comes into close contact with a payment machine. A microchip was first implanted into a human back in 1998, but it. Around the size of a grain of rice, the chips typically are inserted into the skin just above each user's thumb, using a syringe similar to that used for giving vaccinations.
RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already cheap and available, provide a digital interface to the real world centered about the holder’s identity: your ID, credit card information, bus pass, library card, and many other sources of information you currently carry in your purse/wallet can instead be stored on an .
Self-described “bio-hackers” are voluntarily injecting radio frequency identification chips under their skin, which allows them to pay for purchases by just hovering their bare hand over a scanner at a checkout counter.
A chip is implanted underneath the skin between the thumb and forefinger within seconds. 32M claims it is the first company in the US to have offer implanted chip technology to employees. Microchip in Humans - Passport for everything.
Mr Paumen has a chip under the skin of his left hand, and it lights up when it comes into close contact with a payment machine. A microchip was first implanted into a human back in 1998, but it.
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical terms, a. First, the RFID chips are passive – they can’t be tracked since they don’t emit signals. Second, in order to activate the chip implant you have to touch it to a reader; and while someone can scan it without your consent, they would have to get up close since the chips can’t be read at a distance.
Learn how to program the Hyundai NFC digital key for use with the Hyundai .
rfid chips in skin|Human Microchipping: An Unbiased Look at the Pros and Cons