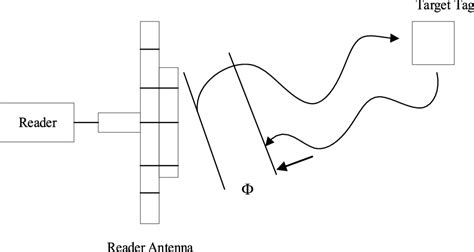
indoor tracking using rfid with topology Within the array of localized objects, we can randomly select a single object for the explicit purpose of tracking. The depiction of the RFID tag/object localization using the devised system is presented in figure 6. It was observed that as the tracked object moves farther from the RFID antenna, there is a noticeable decline in signal strength. Nintendo 3DS NFC Reader / Writer for Amiibo complete New in Box NIB. Brand New. C .
0 · Optimizing indoor localization precision: advancements in RFID
1 · Fingerprinting‐Based Indoor Localization in a 3 × 3 Meter Grid
$21.76
Within the array of localized objects, we can randomly select a single object for the explicit purpose of tracking. The depiction of the RFID tag/object localization using the devised system . Consequently, indoor positioning technology has emerged as a focal point in academic and industrial research [3-5]. The widespread use of technologies such as smart .
Within the array of localized objects, we can randomly select a single object for the explicit purpose of tracking. The depiction of the RFID tag/object localization using the devised system is presented in figure 6. It was observed that as the tracked object moves farther from the RFID antenna, there is a noticeable decline in signal strength.
rfid chips en humanos ventajas y desventajas
Consequently, indoor positioning technology has emerged as a focal point in academic and industrial research [3-5]. The widespread use of technologies such as smart terminals and cellular networks has accelerated progress in indoor positioning, further propelled by the affordability and versatility of emerging 5G and 6G systems. In this paper, indoor location technology based on RFID is selected, and several commonly used location algorithms are introduced in detail. Combined with the latest research, several improved RFID positioning systems are summarized, which improve positioning accuracy and . This study offers a new approach to real-time indoor positioning using passive RFID technology to estimate the real-time location of smart home users based on their movements in smart environment space. Passive RFID: The tag only activates when it comes close to an RFID reader. The reader generates an electromagnetic field, powering the tag and allowing it to send information. Active RFID: The tag has its own power source, so it actively sends out signals at regular intervals, making it suitable for long-range tracking. Accuracy: RFID can locate items within a .
In this paper, we study the detection of highly influential positions from indoor position-tracking data, e.g., to detect highly influential positions in a business center, or to detect the hottest shops in a shopping mall according to users’ indoor position-tracking data.
Optimizing indoor localization precision: advancements in RFID
Amongst the technologies supporting indoor positioning and navigation, radio frequency (RF) based approaches found a particularly significant position due to their ubiquity and low-cost. The presented work demonstrates how the integration of passive Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tracking technology and Building Information Modeling (BIM) can assist indoor localization for potential applications in facilities management for proactive preventative maintenance. Methods.
Researchers have broadened the focus of RFID technology development because to the growing need for low-cost edge devices to bridge the physical-digital gap. In. In this project, we implemented an RFID-based mobile object tracking system on Qualnet simulator and studied two challenging problems in applying RFID into a tracking system—(i) anti-collision and high-speed identification of .
Within the array of localized objects, we can randomly select a single object for the explicit purpose of tracking. The depiction of the RFID tag/object localization using the devised system is presented in figure 6. It was observed that as the tracked object moves farther from the RFID antenna, there is a noticeable decline in signal strength.
Consequently, indoor positioning technology has emerged as a focal point in academic and industrial research [3-5]. The widespread use of technologies such as smart terminals and cellular networks has accelerated progress in indoor positioning, further propelled by the affordability and versatility of emerging 5G and 6G systems. In this paper, indoor location technology based on RFID is selected, and several commonly used location algorithms are introduced in detail. Combined with the latest research, several improved RFID positioning systems are summarized, which improve positioning accuracy and .
This study offers a new approach to real-time indoor positioning using passive RFID technology to estimate the real-time location of smart home users based on their movements in smart environment space.
Passive RFID: The tag only activates when it comes close to an RFID reader. The reader generates an electromagnetic field, powering the tag and allowing it to send information. Active RFID: The tag has its own power source, so it actively sends out signals at regular intervals, making it suitable for long-range tracking. Accuracy: RFID can locate items within a . In this paper, we study the detection of highly influential positions from indoor position-tracking data, e.g., to detect highly influential positions in a business center, or to detect the hottest shops in a shopping mall according to users’ indoor position-tracking data. Amongst the technologies supporting indoor positioning and navigation, radio frequency (RF) based approaches found a particularly significant position due to their ubiquity and low-cost.
The presented work demonstrates how the integration of passive Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tracking technology and Building Information Modeling (BIM) can assist indoor localization for potential applications in facilities management for proactive preventative maintenance. Methods.Researchers have broadened the focus of RFID technology development because to the growing need for low-cost edge devices to bridge the physical-digital gap. In.
rfid chips in humans 2015

Fingerprinting‐Based Indoor Localization in a 3 × 3 Meter Grid
rfid chip sweden
Hi everyone, I'm trying to decode NFC-A ( 13.56Mhz ) data from the HackRF. using C/C++ code instead of GNU Radio, mostly because I want to understand. the logic of demodulation and decoding itself instead of using pre made. tools. I think this is a great goal, but have you .
indoor tracking using rfid with topology|Optimizing indoor localization precision: advancements in RFID