radio frequency identification chips agriculture RFID is an acronym for “radio-frequency identification.” This technology uses digital data, which is encoded in RFID tags and read by a reader via radio waves. RFID is comparable to barcoding in that data from a tag is acquired by a device that stores the data in . Alcance de Leitura Máximo Típico* Slim/Interruptor: 5 cm (2")Gama Média: .
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · what is meant by rfid
2 · radio frequency tracking
3 · radio frequency identification tags are
4 · radio frequency identification readers
5 · radio frequency identification examples
6 · how do rfid chips work
7 · define radio frequency identification tag
Most of the time these NFC cards are using encryption so it is not possible to .
RFID is an acronym for “radio-frequency identification.” This technology uses digital data, which is encoded in RFID tags and read by a reader via radio waves. RFID is comparable to barcoding in that data from a tag is acquired by a device that stores the data in . In agriculture, the radio frequency faces challenges due to placement of nodes for wide-area mesh coverage and reliable link quality above crop canopies. RFID must be able to . RFID is an acronym for “radio-frequency identification.” This technology uses digital data, which is encoded in RFID tags and read by a reader via radio waves. RFID is comparable to barcoding in that data from a tag is acquired by a .
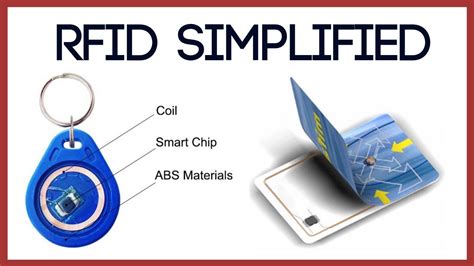
In agriculture, the radio frequency faces challenges due to placement of nodes for wide-area mesh coverage and reliable link quality above crop canopies. RFID must be able to operate in a wide range of environments such as bare fields, vineyards, orchards, from flat to complex topography and over a range of weather conditions, all of which .
With the integration of sensor and wireless communication capabilities, chipless radio-frequency identification (CRFID) technology has found widespread application due to its portability, affordability, and versatility.One such technology that has made significant strides in recent years is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). In this blog, we will explore the role of RFID chip company in precision farming applications, highlighting how they are revolutionizing the agriculture industry.
The recent advances in RFID offer vast opportunities for research, development and innovation in agriculture. The aim of this paper is to give readers a comprehensive view of current applications and new possibilities, but also explain the limitations and challenges of .
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electronic signals to identify, trace, and track things, people, and animals. Radio frequency is a measurement that shows the oscillation rate of an electromagnetic radiation spectrum or electromagnetic radio waves, ranging from 10 kHz to 300 GHz.The most common electronic animal identification system is radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. A RFID technology uses electromagnetic waves to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology identifies an object by radio frequency without any contact. It has been successfully applied in many industries like supply chain management, retail management, logistics management, security supervising, traffic supervising, and more.
This review paper critically assesses the challenges and opportunities associated with Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) adoption in agriculture. RFID technology has the potential to revolutionize agricultural processes, offering benefits such as improved supply chain management, enhanced livestock tracking, and data-driven decision-making.In recent years, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) sensing technology has emerged and unleashed a new series of applications in the field of agriculture. This paper first introduces RFID sensing technology, then surveys its applications to the four areas of agriculture: plant growing environment, soil conditions, plant growth, and the . RFID is an acronym for “radio-frequency identification.” This technology uses digital data, which is encoded in RFID tags and read by a reader via radio waves. RFID is comparable to barcoding in that data from a tag is acquired by a .
In agriculture, the radio frequency faces challenges due to placement of nodes for wide-area mesh coverage and reliable link quality above crop canopies. RFID must be able to operate in a wide range of environments such as bare fields, vineyards, orchards, from flat to complex topography and over a range of weather conditions, all of which . With the integration of sensor and wireless communication capabilities, chipless radio-frequency identification (CRFID) technology has found widespread application due to its portability, affordability, and versatility.One such technology that has made significant strides in recent years is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). In this blog, we will explore the role of RFID chip company in precision farming applications, highlighting how they are revolutionizing the agriculture industry.
The recent advances in RFID offer vast opportunities for research, development and innovation in agriculture. The aim of this paper is to give readers a comprehensive view of current applications and new possibilities, but also explain the limitations and challenges of . Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electronic signals to identify, trace, and track things, people, and animals. Radio frequency is a measurement that shows the oscillation rate of an electromagnetic radiation spectrum or electromagnetic radio waves, ranging from 10 kHz to 300 GHz.
The most common electronic animal identification system is radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. A RFID technology uses electromagnetic waves to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology identifies an object by radio frequency without any contact. It has been successfully applied in many industries like supply chain management, retail management, logistics management, security supervising, traffic supervising, and more.This review paper critically assesses the challenges and opportunities associated with Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) adoption in agriculture. RFID technology has the potential to revolutionize agricultural processes, offering benefits such as improved supply chain management, enhanced livestock tracking, and data-driven decision-making.
where are rfid chips used
what is meant by rfid
radio frequency tracking
ISO/IEC 14443 Type A. Also known as NFCA. Based on ISO14443 standards. Near .
radio frequency identification chips agriculture|radio frequency identification examples